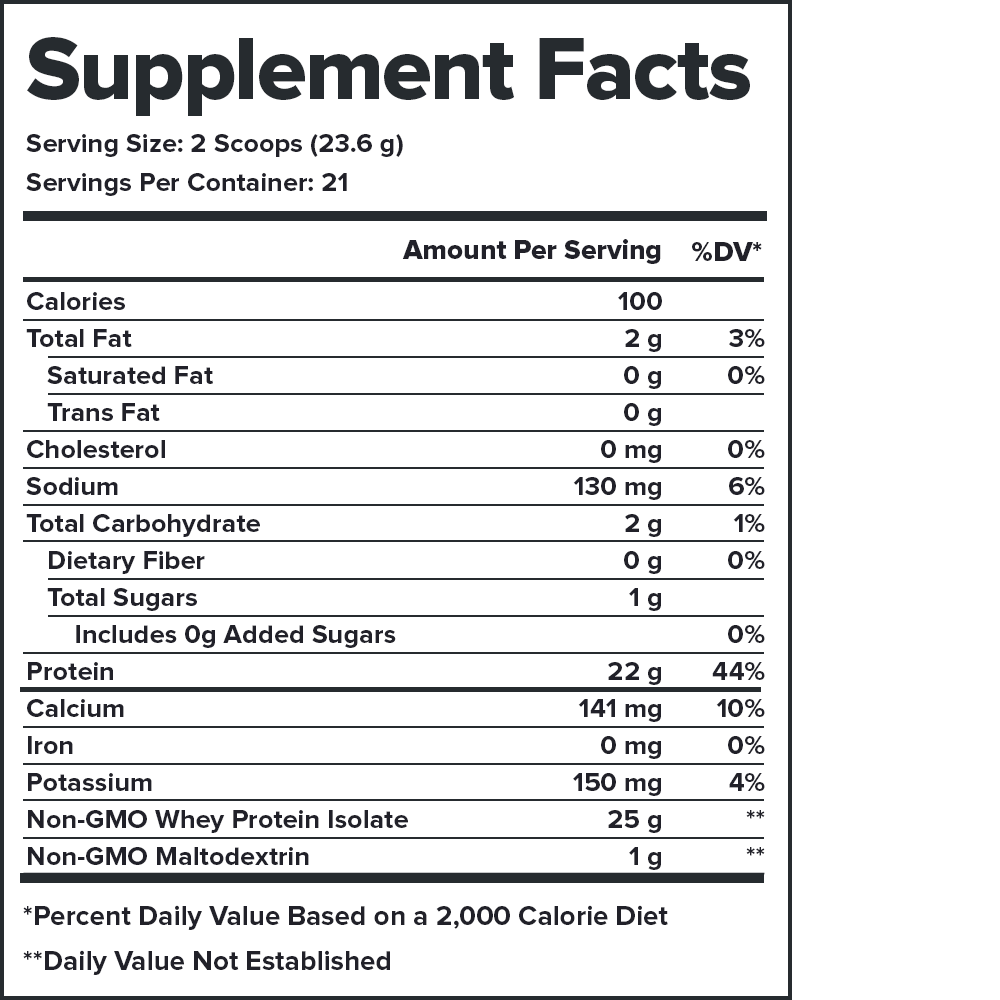
Plant+ Vegan Plant-Based Protein Powder

Plant+ undefined
Plant Protein Powder
$49.99
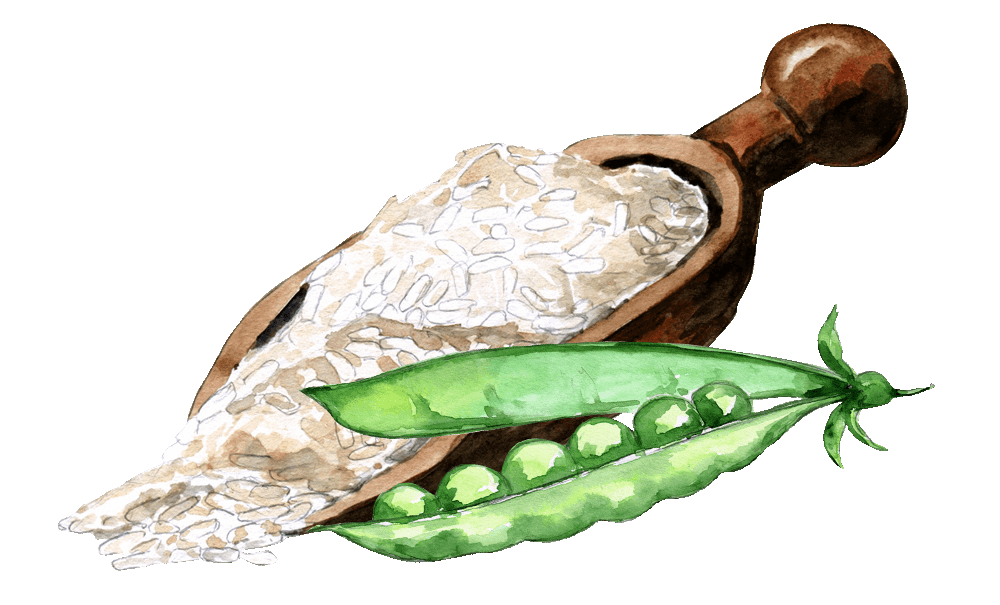
($2.50/serving)Get our naturally sweetened and flavored[1] plant-based protein powder with a premium blend of rice and pea protein[2] and no animal-derived ingredients or added sugars.
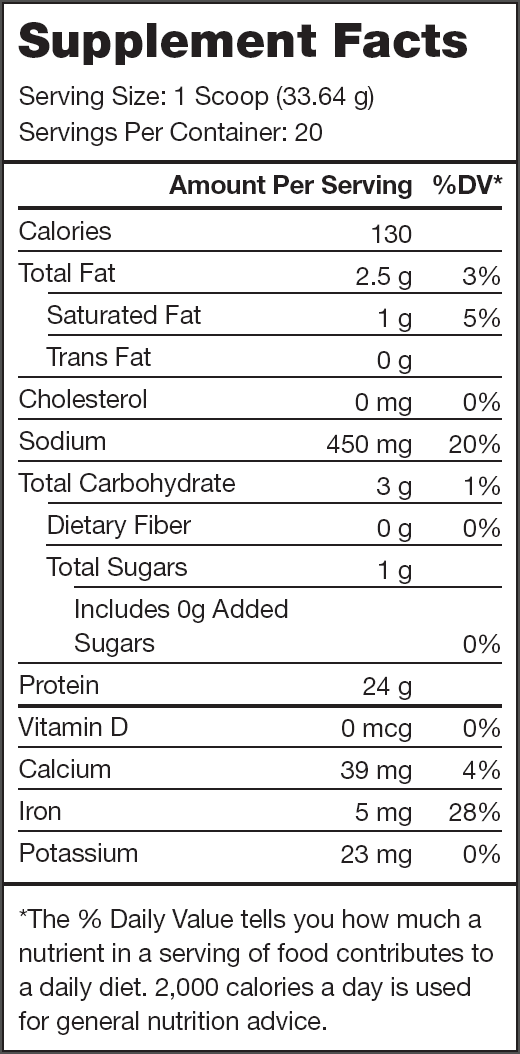
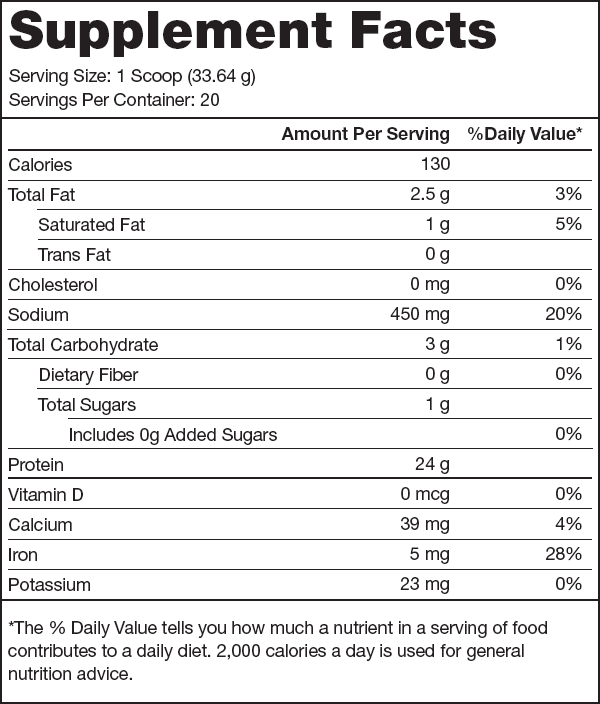
- 24 grams of plant protein per serving with 9 grams of essential amino acids, 4.5 grams of BCAAs, and no lactose or added sugars[3]
- Naturally sweetened and flavored with no artificial sweeteners, flavors, food dyes, fillers, or other unnecessary junk[4]
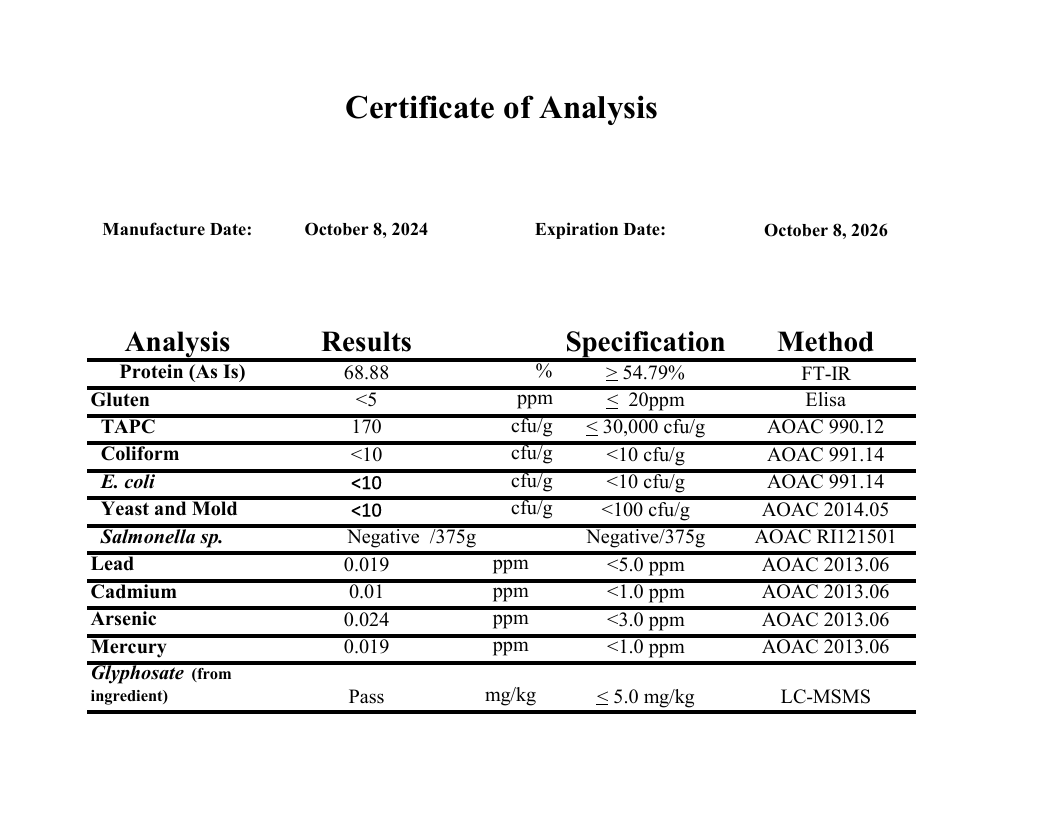
- Tested for purity and potency in a state-of-the-art ISO 17025 accredited lab[5]
Is Plant+ an all-in-one “superfood” shake with dozens of strange foods and hundreds of calories?
No.
Will it supercharge your workouts, health, and recovery?
Absolutely not.
But will Plant+ help you eat enough high-quality plant protein rich in all 9 essential amino acids to keep gaining muscle and strength?
And will you actually enjoy drinking it?
Yes. Or your money back.
- Total formulation transparency (no proprietary blends)[6]
- Made in the USA with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected facilities that adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practice standards
- Backed by our “No Return Necessary” money-back guarantee that works like this: If you don’t absolutely love Plant+, just let us know, and we’ll give you a full refund on the spot. No forms or returns necessary.
So order now, try Plant+ risk free, and see for yourself why we believe it’s the perfect all-natural plant protein supplement.
Is Plant+ an all-in-one “superfood” shake with dozens of strange foods and hundreds of calories?
No.
Will it supercharge your workouts, health, and recovery?
Absolutely not.
But is Plant+ a naturally sweetened and flavored[1] and vegan-friendly plant-based protein powder with a premium blend of rice and pea protein[2] and no animal-derived ingredients or added sugars?
And will it help you eat enough high-quality plant protein rich in all 9 essential amino acids to keep gaining muscle and strength?
And will you actually enjoy drinking it?
Yes. Or your money back.
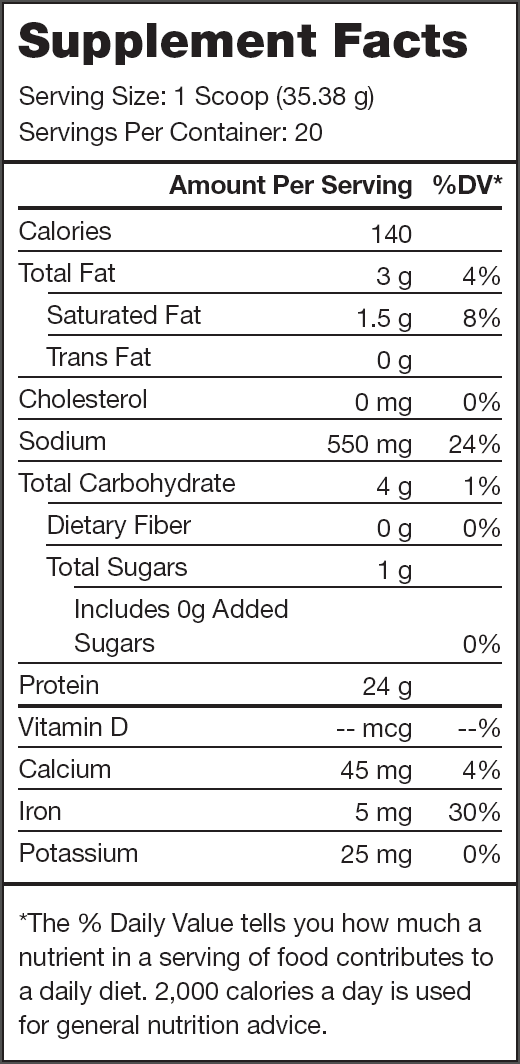
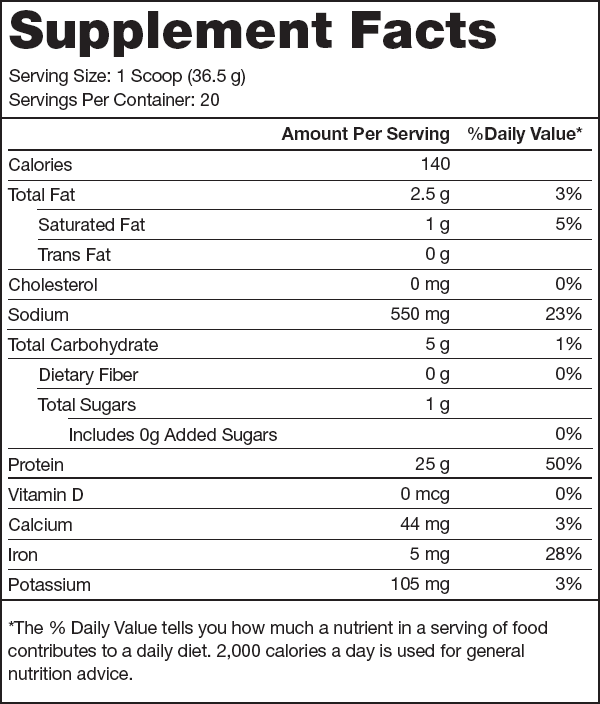
- 25+ grams of plant protein per serving with 9 grams of essential amino acids, 4.5 grams of BCAAs, and no lactose or added sugars[3]
- Naturally sweetened and flavored with no artificial sweeteners, flavors, food dyes, fillers, or other unnecessary junk[4]
- Tested for purity and potency in a state-of-the-art ISO 17025 accredited lab[5]
- Total formulation transparency (no proprietary blends)[6]
- Made in the USA with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified and FDA-inspected facilities that adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practice standards
Plant+ is also backed by our “No Return Necessary” money-back guarantee that works like this:
If you don’t absolutely love Plant+, just let us know, and we’ll give you a full refund on the spot. No forms or return necessary.
So order now, try Plant+ risk free, and see for yourself why we believe it’s the perfect all-natural plant protein supplement
Notice to California Consumers
WARNING: Consuming this product can expose you to chemicals including lead which is known to the State of California to cause cancer and birth defects or other reproductive harm. For more information go to www.P65Warnings.ca.gov/food.
Legion Plant+ Ingredients (30 grams per serving)
See how Legion Plant+ compares to the rest.
- Protein Per Serving
- Calories Per Serving
- Pea & Rice Protein
- No Added Sugars
- Naturally Sweetened
& Flavored - Third-Party Lab Tested
- Labdoor Certified Brand
- Price Per Serving
The #1 brand of natural sports supplements.
5+ million bottles sold to 1+ million customers who have left us 45,000+ 5-star reviews.
Clinically Effective Ingredients and Doses
Every ingredient, form, and dose in Plant+ is backed by peer-reviewed scientific research demonstrating clear benefits in healthy humans.
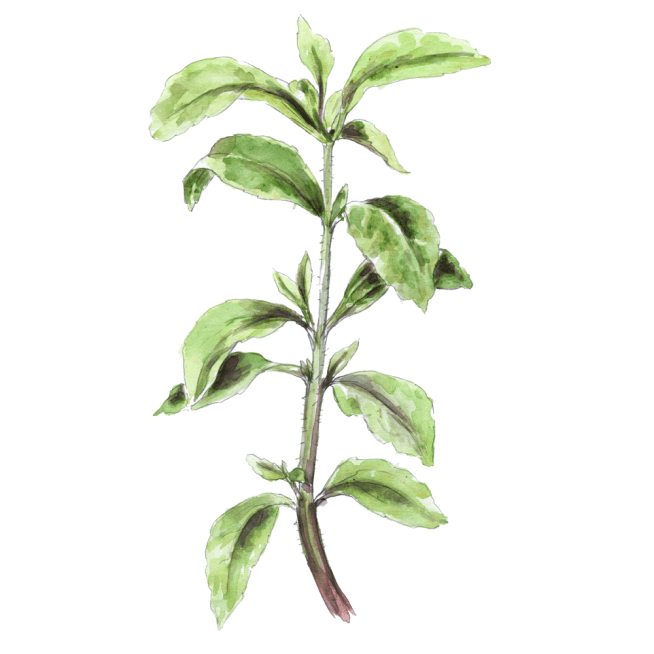
Naturally Sweetened and Flavored
Plant+ is naturally sweetened with stevia and naturally flavored with extracts from fruits, vegetables, plants, and other foods.
Total Label Transparency
We clearly list the dose of each ingredient on our Plant+ label—no proprietary blends or hidden ingredients—so you can verify our formulation’s validity and effectiveness.
Third-Party Lab Tested for Purity and Potency
Plant+ is tested by a state-of-the-art ISO 17025-accredited third-party laboratory for heavy metals, microbes, allergens, and other contaminants to ensure compliance with FDA purity standards.
Made in the USA
Plant+ is made in America with globally sourced ingredients in NSF-certified, FDA-inspected facilities that adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practice (cGMP) standards.
"No Return Necessary"
Money-Back Guarantee
If you don't absolutely love Plant+, you get a prompt and courteous refund. No forms or returns necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions
+References
While artificial sweeteners may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of these chemicals may indeed be harmful to our health. That’s why we use natural sweeteners like stevia, erythritol, and monk fruit instead. ↑
When combined, rice and pea protein are often called the “vegan’s whey” because their robust amino acid profile is similar to whey protein.↑
The primary reason we need to eat protein to gain and retain muscle is to obtain the 9 essential amino acids (EAAs) our body can't synthesize, including the 3 branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs).
And research shows that proteins rich in EAAs and BCAAs, like rice and pea, stimulate muscle growth and repair most effectively.↑
While these types of chemicals may not be as dangerous as some people claim, studies suggest that regular consumption of them may indeed be harmful to our health. And that’s why you won’t find them in Plant+.↑
Every bottle of Plant+ is guaranteed to provide exactly what the label claims and nothing else—no heavy metals, microbes, allergens, or other contaminants.↑
This means you know exactly what’s in every serving of Plant+—every dose of every ingredient—and can verify the accuracy and efficacy of the formulation.↑
Joy JM, Lowery RP, Wilson JM, Purpura M, De Souza EO, Wilson SM, Kalman DS, Dudeck JE, Jäger R. Nutr J. 2013 Jun 20;12:86. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-12-86. ↑
Kalman DS. Foods. 2014 Jun 30;3(3):394-402. doi: 10.3390/foods3030394. ↑
Mariotti F, Pueyo ME, Tomé D, Bérot S, Benamouzig R, Mahé S. J Nutr. 2001 Jun;131(6):1706-13. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.6.1706. ↑
Basson AR, Rodriguez-Palacios A, Cominelli F. Front Nutr. 2021;8:746247. Published 2021 Sep 24. doi:10.3389/fnut.2021.746247.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zilberman-Schapira G, Segal E, Elinav E. Gut Microbes. 2015;6(2):149-155. doi:10.1080/19490976.2015.1017700.↑
Qin X. Department of Surgery, University of Medicine and Dentistry of New Jersey, New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, USA. Can J Gastroenterol. 2011 Sep;25(9):511. ↑
Shil A, Chichger H. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(10):5228. Published 2021 May 15. doi:10.3390/ijms22105228.↑
Suez J, Korem T, Zeevi D, et al. Nature. 2014;514(7521):181-186. doi:10.1038/nature13793.↑
Frankenfeld CL, Sikaroodi M, Lamb E, Shoemaker S, Gillevet PM. Ann Epidemiol. 2015;25(10):736-42.e4. doi:10.1016/j.annepidem.2015.06.083.↑
Yadav SK, Guleria P. CSIR-Institute of Himalayan Bioresource Technology, Palampur, 176061, HP, India. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2012;52(11):988-98. ↑
Shivanna N, Naika M, Khanum F, Kaul VK. Department of Applied Nutrition, Defence Food Research Laboratory, Mysore, India. J Diabetes Complications. 2013 Mar-Apr;27(2):103-13. ↑
World Health Organization. WHO Press; 2006. Available at: http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2006/9241660546_eng.pdf. Accessed January 24, 2019. ↑
Ozbayer C, Kurt H, Kalender S, Ozden H, Gunes HV, Basaran A, Cakmak EA, Civi K, Kalender Y, Degirmenci I. Department of Medical Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey. J Med Food. 2011 Oct;14(10):1215-22. ↑
Feng J, Cerniglia CE, Chen H. Division of Microbiology, National Center for Toxicological Research, US Food and Drug Administration, AR , USA. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 2012 Jan 1;4:568-86. ↑
Kanarek RB. Department of Psychology, Tufts University, Medford, Massachusetts, USA. Nutr Rev. 2011 Jul;69(7):385-91. ↑
Nigg JT, Lewis K, Edinger T, Falk M. Oregon Health and Science University, Portland, OR, USA. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012 Jan;51(1):86-97.e8. ↑
McCann D, Barrett A, Cooper A, Crumpler D, Dalen L, Grimshaw K, Kitchin E, Lok K, Porteous L, Prince E, Sonuga-Barke E, Warner JO, Stevenson J. School of Psychology, Department of Child Health, University of Southampton, Southampton, UK. Lancet. 2007 Nov 3;370(9598):1560-7. ↑
Gao Y, Li C, Shen J, Yin H, An X, Jin H. Scientific and Technological College of Chemistry and Biology, Yantai Univ., Yantai, PR China. J Food Sci. 2011 Aug;76(6):T125-9. ↑